There are several use cases that Financial Information Users (FIU) can build in the Account Aggregator ecosystem. The conventional use cases listed below are currently in production and can be significantly improved.
- Lending
- Wealth Management
- Personal Finance Management Apps
- Robo Advisory
- Reconciliation of Accounts
While we have listed five use cases, the ecosystem continues to innovate and develop new products and services.
1. Lending Use Case
A borrower provides their banking and other data to the lender either by sharing hard copies or PDF documents. This method is not ideal, as it is time-consuming for the borrower to collect and submit the data. The lender must process the data using the screen scraping method, and this process of data sharing is not tamper-proof.
Banks and NBFCs should use the opportunity of AA to increase the velocity of safe lending.
- AA enables speedy data access, allowing NBFCs to process more loan applications faster.
- Lenders using Account Aggregators can receive data about the borrower in real-time, which is digitally signed by the Financial Information Provider (FIP), such as the borrower’s bank.
- AAs can help lenders derisk their loan book. Reduce NPAs!
- Lenders can offer their customers personalized and customized loan products.
- And a crucial feature of AAs is loan monitoring. Lenders can now monitor loan accounts post-disbursement for early intervention and lower loan loss provision.
1.1 Cash Flow Lending
When it comes to credit bureau files in India,
- 200 million individuals have thick files, meaning there is a substantial amount of data to generate a credit score.
- 170 million have thin files
- A whopping 190 million have no file.
AAs allow lenders to access underserved segments: Only 19% of MSMEs in India have access to formal credit! Lending based on borrower’s business cash flow is a significant opportunity in unsecured lending.
The AA framework, in conjunction with the upcoming Public Credit Registry (PCR), enables lenders to offer sachet-sized loans based on a business’s cash flow.
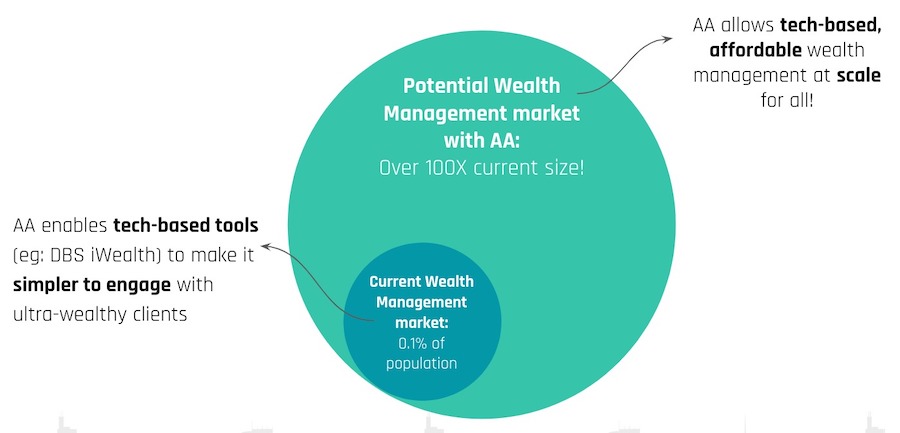
2. Wealth Management Use Case
Wealth managers in India largely depend on their clients to submit data on a periodic basis. The client has the option to share credentials with the wealth manager, which facilitates the smooth sharing of the data, however, this is not the most secure method.
A data principal (wealth manager’s client) can give a recurring consent to an AA to share data from select FIPs with the wealth manager. This method has several advantages,
- The data principal does not have to share the FIP’s credentials (login, password)
- The wealth manager is not dependent on their client to share data
- The data received by the wealth manager is in digital format. It can be fed directly to the wealth manager’s platform and generate actionable reports.
The wealth management market in India is relatively small, and has the potential to expand significantly. AAs can help grow this market as wealth managers can devote more time to acquire clients while technology aids in their day-to-day operations.
3. Personal Finance Management Apps Use Case
The usage of personal finance management (PFM) apps in India is low. Possibly, most believe we “know our finances” and do not need help. There are a few PFM apps in India that access a users’ bank account statements by one of the following methods,
- User uploads PDF documents
- User shares the login credentials with the app
Neither of the above methods is ideal from a privacy perspective.
An individual makes about 200 financial decisions in their lifetime – choosing a bank to open a savings account, home loan, personal loan, buying/selling mutual funds, and insurance policies. Good PFM apps help individuals make better financial decisions. It is essential for PFM apps to not only graphically represent data but also provide actionable reports.

3. Robo Advisory Use Case
Although millennials prefer Robo-advisory-type solutions, they are still relatively new in India. The success of robo-advisory will depend on the quality of their algorithms.
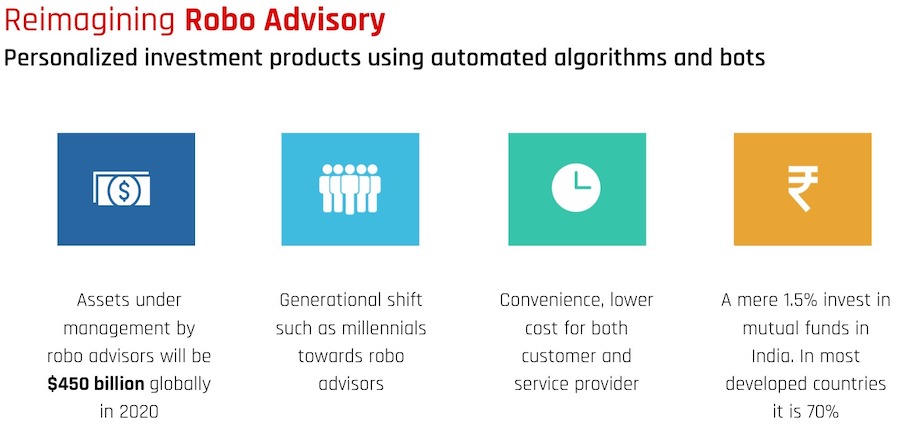
Mutual Fund investments in India are increasing through robo-advisory apps. If these apps have real-time access to a users’ financial data, they can improve informed decisions. A few of the features of robo-advisory apps are,
- Portfolio Assessment and Rebalancing Recommendations
- Switch to Direct
- Analytics on Investments
In the current setup, collecting data is cumbersome and requires several steps to acquire, extract, and process it. In the AA world, robo advisors will receive digital data directly from data fiduciaries (FIPs, such as banks, mutual fund depositories, and insurance companies).
5. Reconciliation of Accounts Use Case
India has 63 million MSMEs. As per the MSME committee report, they contribute approximately 30% to our GDP. The majority of MSMEs are in the manufacturing sector.
Any well-run MSME would like to close its accounts daily. MSMEs utilize financial accounting packages, including Tally, QuickBooks, and others. The owner or accountant enters banking transactions and invoices into the accounting package. It’s a key financial control that enables the owner/proprietor to know the actual state of cash they have in hand.
Currently, only entities regulated/registered with a financial regulator can participate in the AA ecosystem.
| Reconciliation in Pre-AA Era | Reconciliation in AA Era |
|---|---|
| MSMEs reconcile between the transactions in their physical books and bank passbooks. | Accounting package downloads bank statements using an Account Aggregator with business owner’s consent. |
| MSMEs started using financial accounting packages and reconciled with bank passbooks or printed bank statements (received by email). | Bank statement data received is in real-time and has no data errors. |
| MSMEs can use financial accounting packages but have to share their net banking credentials or bank statements in diverse formats. | Books Reconciliation happens in real-time with no security risk. In addition, the standardised format of AA solves for the current diversity in bank statement formats. |
| The MSME employs a clerical staff to get the digital statement from the bank and upload it into the accounting software. Since this is not a dedicated job for the person, the quality of reconciliation is not great and hence doesn’t help the proprietor know the amount of real cash the business has. | Books Reconciliation happens in real-time with no human intervention and no security and privacy risks. |
Related Readings
- Account Aggregator Use Case for Payment Aggregators
- What is an Informed Consent & Consent Artefact?
- Loan Monitoring Use Case For Account Aggregator Framework
- Account Aggregators – Making Investing and Borrowing Simpler
- Unified Nominations Register (UNR) with Account Aggregator Framework
- Prevalent Use Cases in the Account Aggregator Ecosystem